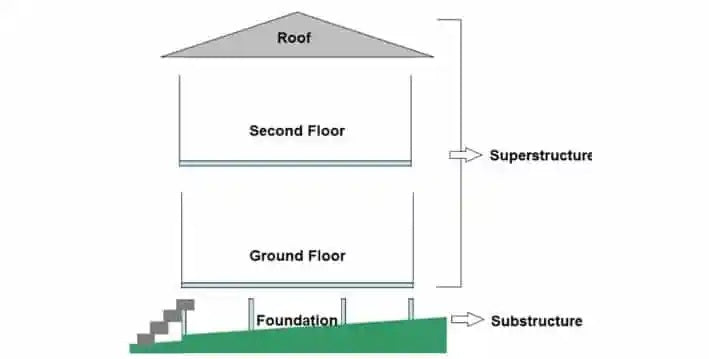
Residential buildings are made up of two major components: the superstructure and the substructure.
The superstructure is part of a building that is constructed above ground level, while the substructure refers to the part of the building built below ground level.
Therefore, the superstructure is made up of several parts and rooms that are interconnected to provide usable living space.
Here is everything you need to know about superstructures.
What is a superstructure?

The superstructure is part of a building where people spend most of their time, including all the floors inside a home and those inside larger buildings.
The term "superstructure" refers to all the parts of a building constructed above the ground that serves the structure's intended use.
The parts of a building that form a superstructure include the floors, roof, columns, slabs, beams, all finishes, doors, windows, flooring, lintels, and parapets.
How does it compare to a substructure?

Source -
While a superstructure is where the building serves its intended purpose of occupation, a substructure is the part of a building constructed below ground level to support the superstructure.
A substructure transfers the weight load of the superstructure into the ground underneath. Therefore, it is important to ensure that all support elements like walls, beams, columns, and foundations are well incorporated into the substructure so that the superstructure is well anchored.
A substructure also prevents the superstructure from coming in direct contact with moisture from the ground, which can weaken it over time.
A building requires both a superstructure and a substructure to be considered safe, stable, and durable. The parts of a building that make up the substructure include the plinth and foundation.
What parts of a building make up the superstructure?
A superstructure consists of every part of a building that is constructed above the ground level. These parts include the walls, beams, columns, windows, doors, floors, roof, finishing, and any other parts of the usable structure of a building.
Floors
A floor is the part of a superstructure that provides a flat living surface and separates different levels of a building. Floors allow people to walk around, place furniture, and store many items.
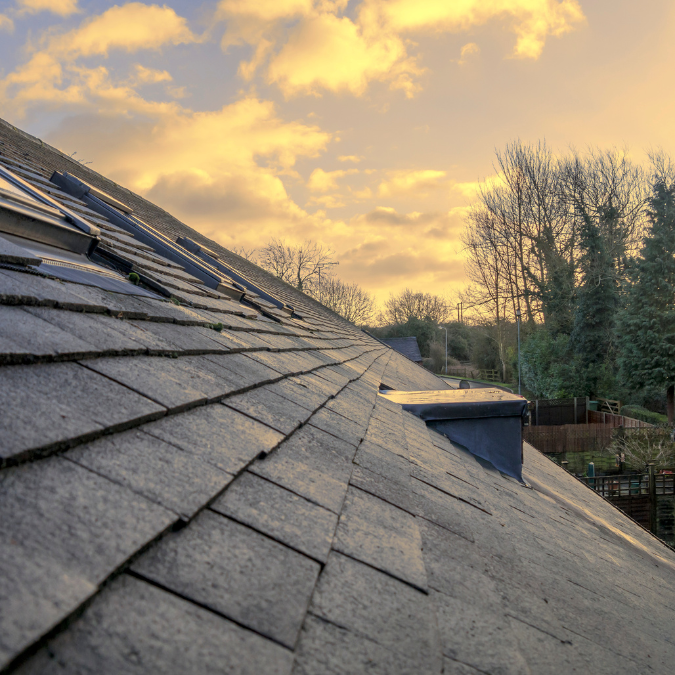
Roof
A roof is a protective cover for a building made of tiles, metal sheets, or a slab that protects the interior of a house from the outdoor elements.
The type of material used on a roof can affect sound and heat insulation, in addition to the look and maintenance of the building. Roofs can help with energy efficiency, as a homeowner can use them to mount solar panels and gain access to renewable energy.
Roofs can also accommodate MEP equipment like water tanks and water heater tanks. This can save you valuable space inside the house that can be repurposed to maximize living spaces.
Lintels
A lintel is a horizontal support made of timber, stone, concrete, and steel used to support the wall in large openings. The width of a lintel often corresponds with the weight of the wall.
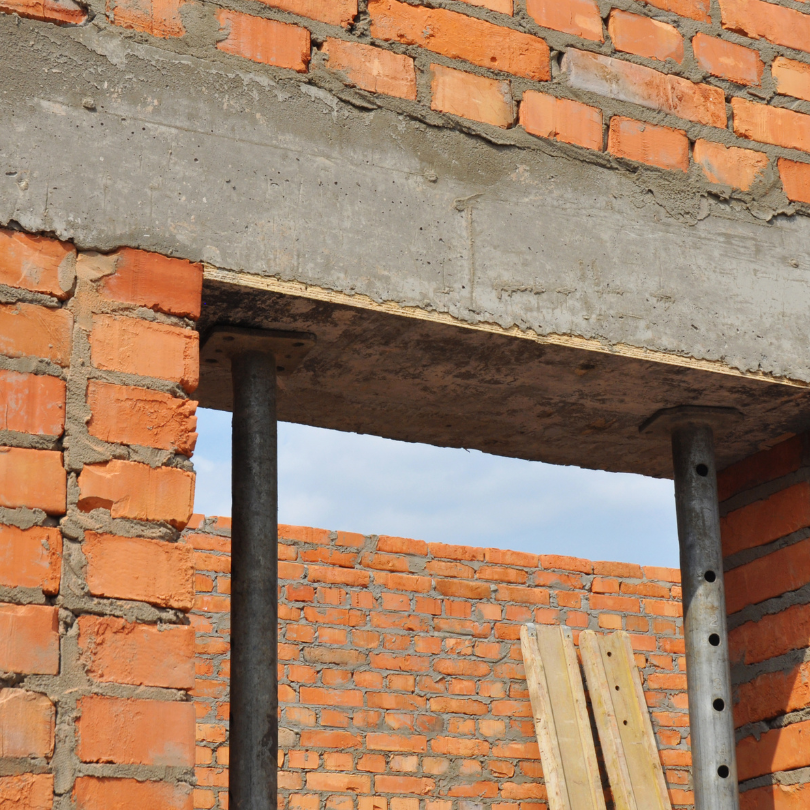
Beams
A beam is a horizontal construction element designed to withstand vertical loads and bending movements. It is used to provide a safe load path to distribute the weight of a structure to the walls and the foundation.
Columns
A column is a vertical reinforced support structure that can hold a lot of weight to ensure the weight from the upper parts of a building is transferred to the foundation and the ground.
Walls
Walls are vertical reinforced surfaces that are used to define and separate living spaces from one another and are used to separate indoor areas of a building from outdoor areas.
Walls are constructed from concrete and masonry which allows them to hold the weight of roofs, slabs, beams and other construction elements.
Parapets
A parapet is a low protective external wall that extends past a roof slab. It is used to provide a safe spot for occupants who are on the roof and also to prevent water from spilling over the edge of a roof over the entrance of a building.
Other parts of the superstructure include:
- Stairs, ramps, lifts, and vertical transportation elements.
- Doors, windows, and other openings.
These parts make a superstructure collectively larger and lengthier than a substructure. This results in the superstructure being much larger and heavier than the substructure.
What are the functions of a superstructure?
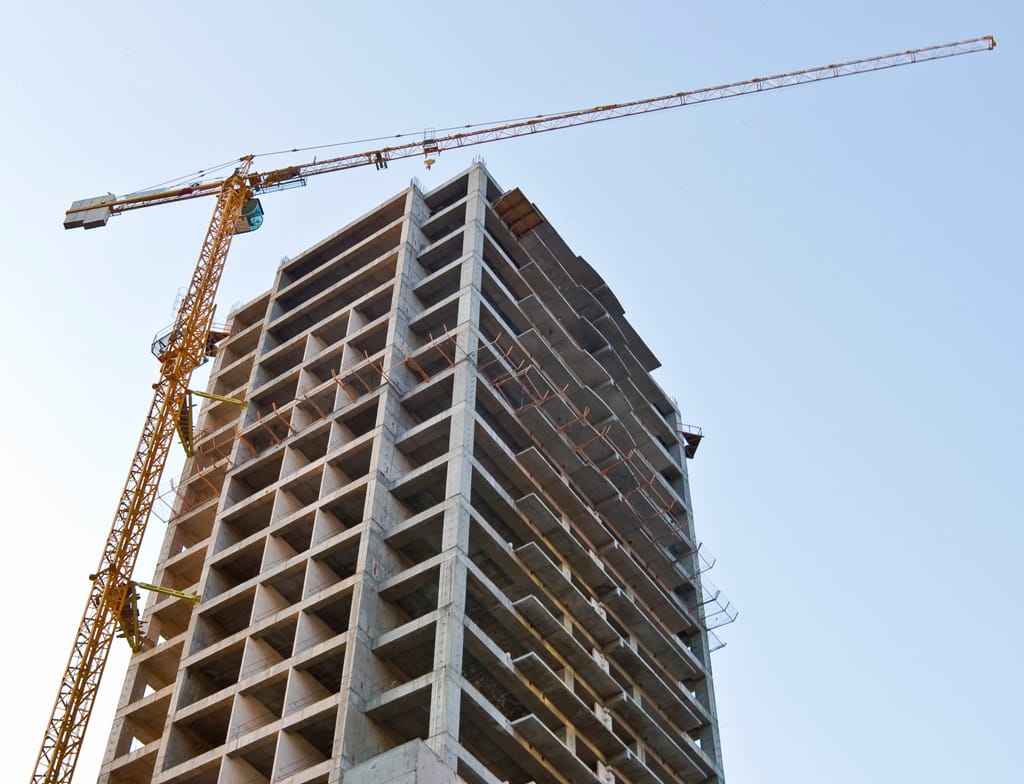

A superstructure provides the occupants with the main living spaces and protects the interior from outdoor elements like harsh weather, animals, and intruders.
A superstructure also serves the important function of transferring the load from the upper parts of a building into the substructure so that the whole building is upright and well anchored into the ground.
Types of Superstructures

The term superstructure includes;
- The frame of the house, which encompasses the load-bearing framework, the main floor, roof beams, roof trusses, ties, casings and stanchions.
- The upper floors, suspended floors in basements, service floors, walkways, top landings, and balconies.
- The roof structure including coverings, drainage, rooflights and other roof features.
- Stairs, ramps, ladders and other features that connect different floors.
- External walls excluding walls to the basement meant to act as retaining walls.
- Openings like windows, doors, hatches and vents.
- Internal walls, partitions, mobile room dividers, cubicles and balustrades
Conclusion
The superstructure is an important part of any building. It is the visible part of a building that sits above the ground level, from the ground level to the top of the structure.
It is worth spending a lot of time and resources to construct a solid substructure that is capable of supporting the superstructure and any items that may be put on the inside of a building.





2 comments
RobertJax
Hey, apologies for disturbing you, but I need some help. My USDT TRX20 is in the OKX wallet, and the recovery phrase is [ clean party soccer advance audit clean evil finish tonight involve whip action ]. What’s the process to transfer it to Binance?
RobertJax
Hello, hope I’m not bothering you, but I need some help. My USDT TRX20 is in the OKX wallet, and the recovery phrase is [ clean party soccer advance audit clean evil finish tonight involve whip action ]. What’s the process to transfer it to Binance?
Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.