It is important to properly anchor and support structural elements during the construction of buildings. One of these important support tools is lintels which are frequently used in all types of buildings.
Here is everything you need to know about lintels in construction.
What is a lintel?

A lintel is a horizontal structure used in openings such as doors, windows, and archways. Lintels support the weight of masonry over the openings in a wall to maintain structural rigidity.
Lintels are crucial in construction because they distribute the weight of the structure above openings to the surrounding walls and columns to prevent them from collapsing under the weight of the materials above them.
What are the functions of lintels?
Lintels support the weight of structures directly above wall openings like doorways and windows. These open spaces often lack structural integrity because they do not have enough support above the gaps to support the weight load on top of the opening.
Without a lintel, the weight above openings in a wall would cause the structure to buckle or collapse, resulting in structural failure that could have catastrophic consequences. Lintels have been used for many years to create strong and durable buildings.
What is the difference between lintels and beams?

Lintels carry the load of the wall above openings and transfer it to the walls near the opening. On the other hand, a beam carries a load from a slab or roof and transfers it to the column, which in turn transfers the weight to the footing and the ground beneath the structure.
What are the types of lintels in construction?
Wood lintel

Wooden or timber lintels have long been considered a supportive and attractive material in construction. However, they have recently become less popular after being replaced by more modern techniques and alternative materials that are more accessible and offer more durability.
Part of this stems from how timber is relatively costly, less durable, and more susceptible to fire compared to other materials.
For longer openings, multiple wooden pieces are joined together using steel bolts to ensure the entire opening is appropriately supported. Other techniques for additional reinforcement involve using flinched lintels and steel plates to support the top and the bottom of the wood.
Stone lintel

Stone lintels are quite common as a result of the general abundance of the material. Stone lintel blocks are available in many customizable shapes and sizes.
An added benefit is that they do not rust over time, unlike steel lintels. However, construction experts advise taking caution when using stone lintels. They have a brittle tensile nature that makes them prone to cracks that develop under vibratory loads like those caused by earthquakes.
Brick lintel
Bricks are only a good option for lintels when the load above the opening is light. The kind of bricks designed for use on lintels have indentations called frogs, which provide more shear resistance at end joints.
Brick lintels are often arched because straight brick lintels are quite weak and prone to failure. The arched shape distributes the weight better to improve the structural strength, reducing the potential for failure.
This method is referred to as a joggled brick lintel.
Reinforced brick lintel
Reinforced brick lintels are stronger than plain brick lintels. For openings that are longer than a meter, steel bars are used to reinforce bricks. The steel rods provide enough additional support to increase the load that bricks can hold above an opening.
These brick lintels are reinforced using steel bars, angle sections, channel sections and double angle sections.
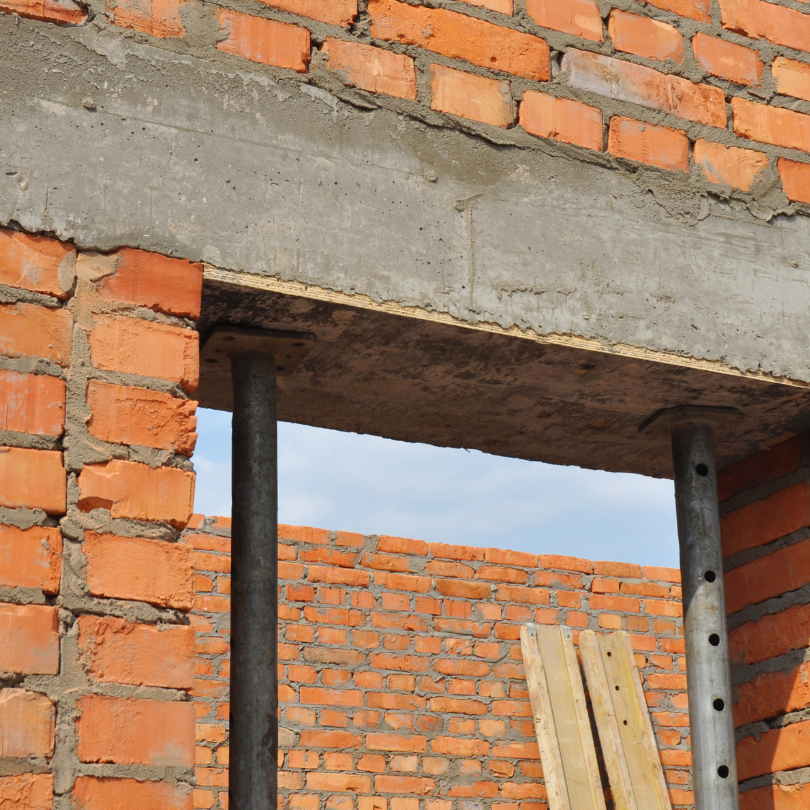
Reinforced concrete lintel
These lintels are made of concrete and have metal bars running along the bottom and sheer stirrups.
Reinforced concrete lintels are a popular choice because they are rigid, have high load-bearing capacity, are affordable, easy to use, and highly resistant to fire.
They are used on doors, windows, and other large openings because of their suitability for all kinds of loads.
Steel lintel

Source -
Steel is an exceptionally useful building material because of its high strength. Channel steel sections and rolled steel joints are intricately combined to make steel lintels.
Steel lintels are used to support heavy superimposed loads and large openings. You can choose from single sections or use them in combination, depending on what your use case demands.
What are the signs of lintel failure?
.jpg?v=300f7aba&mode=h)
source -
Steel lintels are known to be susceptible to pitting and corrosion as a result of rust, which wears down the metal. This can cause the support to fail and pose safety and construction hazards.
If cracks appear in a window, it could be a sign that it is taking some structural weight rather than the lintel.
Another sign of brick and concrete lintel failure is the appearance of cracks around the mortar joints, in the surrounding masonry and depressions along the opening.
Crumbling brickwork and stone lintels is another sign of lintel failure, particularly in areas where humidity and weather than exert pressure on a lintel to make it bend out of shape.
Timber lintels bend downwards to result in an uneven shape on the opening when they are nearing a failure point.
How are lintels maintained?
The maintenance of lintels depends on the type of material used. For steel lintels, you can install flashing during construction to protect against rust and other environmental conditions.
However, if you notice signs of rust along the surface of a lintel, you may need to remove the rust and repaint it.
For steel and stone lintels, proper drainage is important to maintain structural integrity. Signs of water damage include deterioration, cracks, and fissures. The only way of preventing water damage for steel and stone lintels is to ensure that water does not pool around them.
Conclusion
Lintels are placed across the top of openings in a wall and are used to support the weight above these empty spaces like doors and windows.
They are created from a variety of materials such as wood, stone, steel, bricks, and concrete.
Lintels do not only serve structural support purposes, they can also be used ornamentally by carving designs into them and adding decorative elements.
Signs of lintel failure include cracks in windows, in mortar joints of openings, and depressions along the openings themselves. Be sure to look out for these signs to prevent unrecognized failure, as this can cause significant physical harm and costly damage.





Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.